Overview
This project aims to dive deep into the amazing motor controller TMC2209. While researching for my own Voron 3D printer, I came across the need to select a motor controller. I discovered the significant differences between the TMC2209 controller and other ICs like the DRV8825 or A4988. The main differences are the overall driving current, motor protections, and mainly the amazing ultra-low operating sound.
I then developed this evaluation board dedicated to testing the TMC2209 motor driver. Additionally, I explored the use of dual encoders and closed-loop control, ensuring angle closed-loop or speed closed-loop. This driver will be a great addition to my future robotics projects.
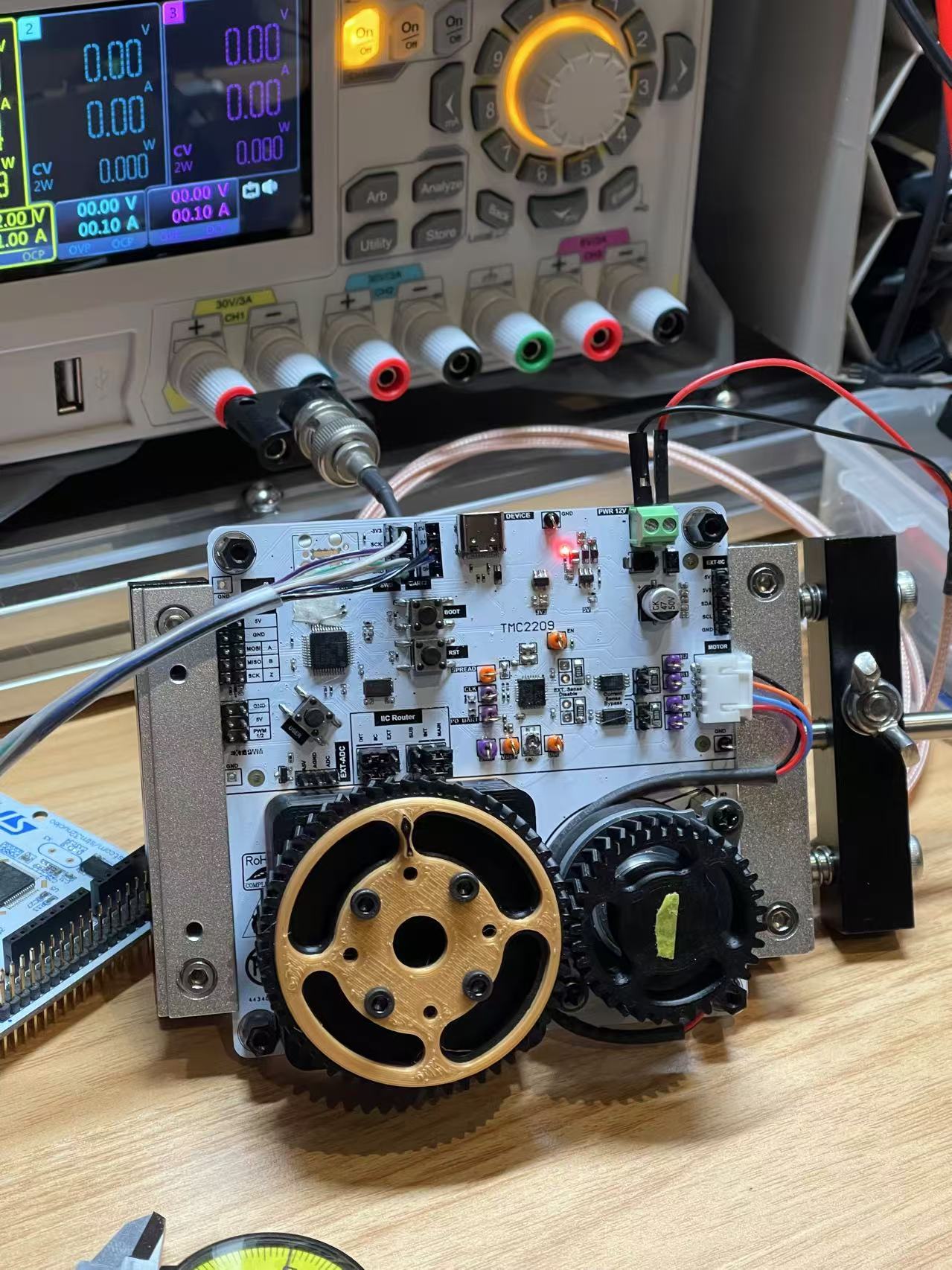
Key Components
- STM32F104 Low-cost MCU: Used for encoder reading, CAN bus message handling, closed-loop calculation, and SPWM generation for the motor controller.
- Dual 16-Bit Magnetic Encoder: A single encoder allows for closed-loop control, while a dual encoder allows saving the absolute zero position into internal ROM flash. This enables the STM32 to know the zero position every time it boots up without losing it.
- TMC2209: The motor driver I want to explore in depth. It has amazing features like CoolStep and StealthChop, which improve micro-stepping performance at the driver level. This results in ultra-low noise operation by reducing stepping current and preventing overstepping, which often causes noise at low speeds.
- CoolStep Technology: This feature dynamically adjusts the motor current based on load conditions, which helps in reducing power consumption and heat generation. It also ensures that the motor runs smoothly and efficiently under varying loads.
- StealthChop Technology: This technology is designed to make the motor run as quietly as possible by optimizing the current waveform. It is particularly useful in applications where noise reduction is critical, such as in 3D printers and other precision equipment.
- SpreadCycle Technology: This is a high-precision chopper algorithm that ensures smooth and precise motor operation. It helps in achieving better torque performance and reduces vibrations, which is essential for high-precision applications.
- MicroPlyer Interpolation: This feature allows for up to 256 microsteps per full step, providing extremely smooth motion and high-resolution control. It is beneficial for applications requiring fine positioning and smooth motion control.
- Simple On-board Gear Design: Allows experimentation with gear ratio motion control and dual encoder reading.
Hardware Design
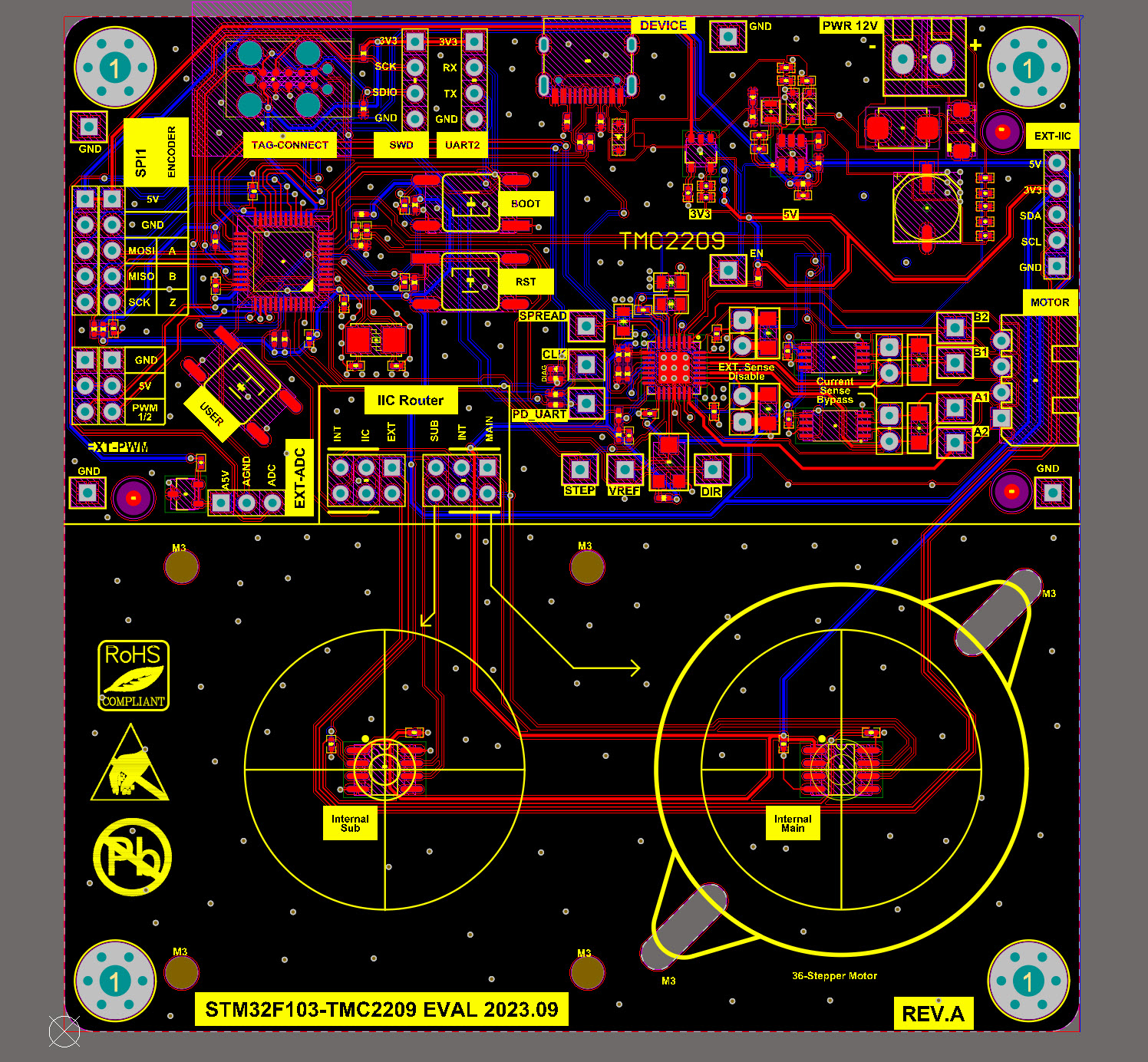
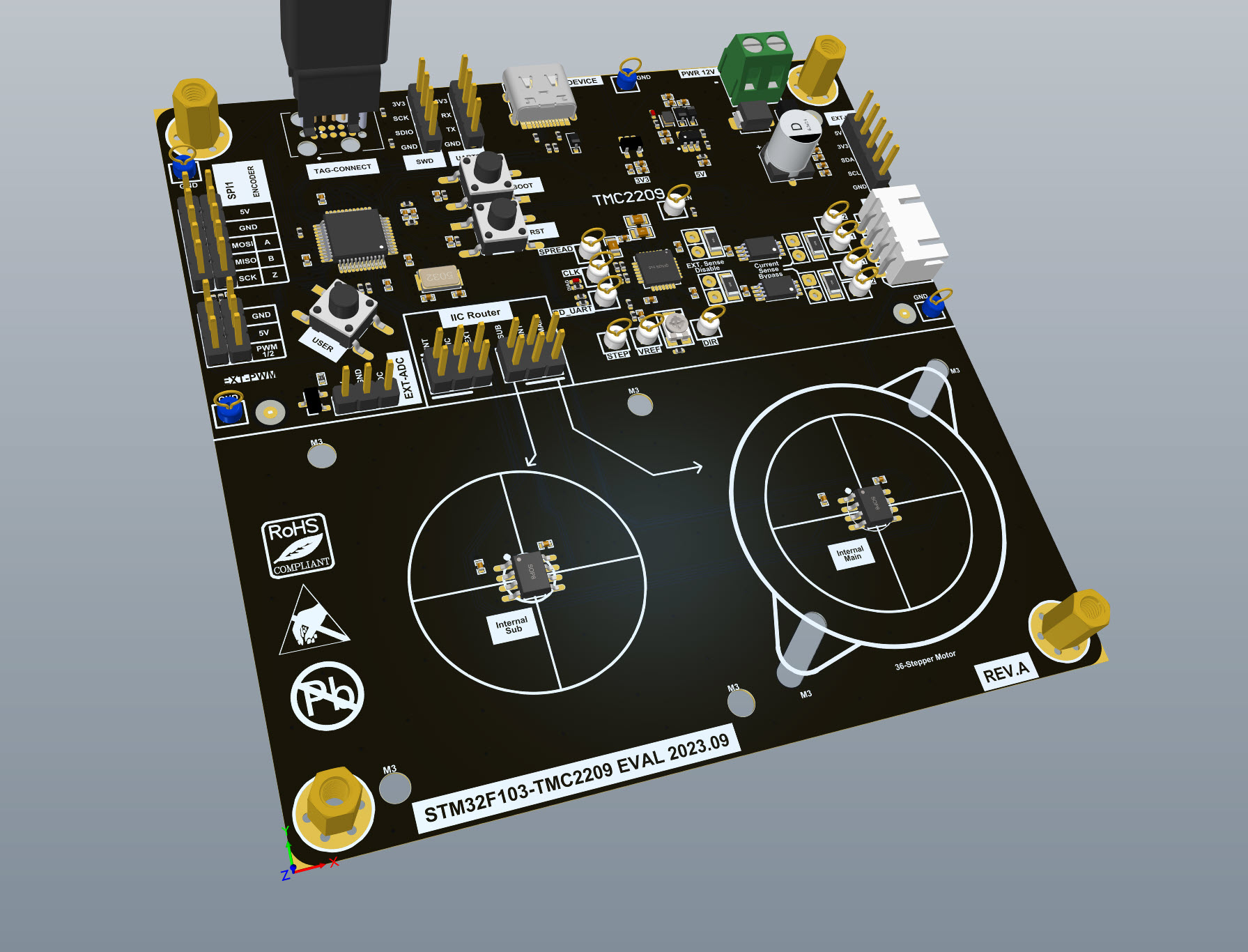
Software Development
- CAN Bus Message Handling: Implementing CAN bus message handling for simple motor controls such as setting angles, reading angles, zeroing, setting up internal closed-loop PIDs, and triggering homing. This allows for simple command interaction and multi-motor control.
- Acceleration Curve Implementation: Although the TMC2209 offers hardware-level acceleration and deceleration, it doesn’t support longer acceleration times. Implementing a good S-curve is critical for SPWM generation to ensure smooth acceleration.
- There are a ton of acceleration algorithms. And some use the advantage of STM32’s DMA, reducing SPWM generation’s interrupt.
- S-Curve Acceleration/Deceleration: Implementing an S-curve acceleration and deceleration algorithm is crucial for smooth motor control. The S-curve profile helps in reducing mechanical stress and achieving smoother motion transitions.
- Logarithmic Curve Acceleration/Deceleration: This method provides a logarithmic acceleration and deceleration profile, which can be beneficial for specific applications requiring non-linear motion control.
- DMA Optimization with STM32: Utilizing the Direct Memory Access (DMA) feature of the STM32 microcontroller can optimize the implementation by reducing the number of interrupts required for SPWM generation. This leads to more efficient and reliable motor control.
- There are a ton of acceleration algorithms. And some use the advantage of STM32’s DMA, reducing SPWM generation’s interrupt.
- Dual Encoder Reading: Reading dual encoders and calculating the absolute zero position based on the saved encoder offset.
- Closed-Loop Control Algorithms: Implementing closed-loop control algorithms for precise motor control. This involves using feedback from the encoders to adjust the motor’s position and speed in real-time, ensuring accurate and stable operation.
Video Demo
This video demonstrates the acceleration process and ultra-low noise performance with TMC2209:
Document Information
- Author: Hsuan Han Lai (Edward Lai)
- Link: https://adwuard.github.io/projects/SilentMotorDriver/
- Copyright: Free to share - Non-commercial - No derivatives - Attribution required (Creative Commons 3.0 License)
